1. Introduction
- System SW 소개
System SW vs Application, History of OS
2. Unix overview
- Unix and Linux : 특징과 장단점, 구성
- Kernel & User mode, logging in, Shell, File system, Program & Process, Error handling, User identification, Signals, Time values
3. Files and directories
- File system = file data + file attribute
- 파일 관련 함수
4. Time and date
- 시간 관련 함수
5. Process control
- Process란, process 상태, identifiers, process termination
- fork, vfork, exit, wait, waitpid, exec
3. Files and directories
overview
< File system = file data + file attribute >
file attribute : Type, permission, size, time, user/group ID
파일 정보
관련 함수 : stat() & fstat() & lstat()
- 파일 정보 get -> return 0 : OK / -1 : error
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf) : file에 대한 information
- int fstat(int filedes, struct stat *buf) : 열려 있는 file information
- int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf) : symbolic link에 대한 자체적 정보, pathname이 sym아니면 stat과 똑같음
관련 구조체
struct stat {
mode_t st_mode; /* file type & mode (permissions) */
inode
device num
links number
uid_t st_uid;
gid_t st_gid;
st_size
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last file status change */
}
관련 변수
st_mode
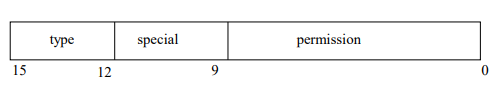
4bit / 3bit / 9bit
- file type : socket, symbolic link, regular, block special, directory, character special, FIFO
- Regular file : 가장 흔함, data 포함, UNIX에서는 data가 text인지 binary인지 구분 x (applications에서 interpret)
- Directory : 다른 파일의 이름과 해당 파일의 정보에 대한 포인터 포함
- Block special file : 고정된 크기의 buffer로 I/O acess (E.g. disk)
- Character special file : 가변 크기 + unbuffered I/O access (E.g. keyboard, mouse)
- FIFO : process간 통신에 사용 ( = pipe )
- Socket : process간 network 통신에 사용
- Symbolic link : 다른 file을 가리킴

- special bits

- permission bits

+ file type macro
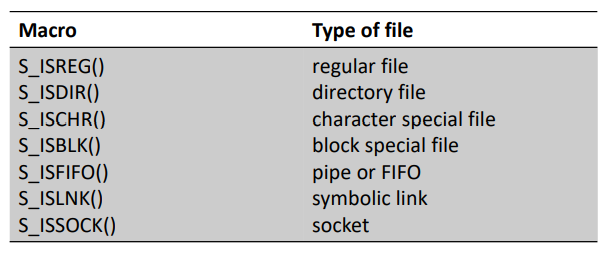
ex) S_ISREG(buf.st_mode) -> 참이면 1 아니면 0
파일 권한
관련 정보 :
- real ID, effective ID
- real user(group) ID : 실제 사용자
- effective user(group) ID : file access permission 결정
- 보통 이 둘은 같지만 setuid(setgid) bit가 set이 되면 달라질 수 있음 -> rws
- 새로운 파일의 user ID는 process의 effective ID로 설정
- File access permissions
- 10bit : 1bit -> -, d, b, c ... , 3bit -> user, 3bit -> group, 3bit -> others

관련 함수 : access(), umask(), chmod()&fchmod()
- 권한 확인 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- int access(const char *pathname, int mode) : mode (R_OK, W_OK, X_OF, F_OK)
- 권한 mask ( return previous file mode creation mask )
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- mode_t umask(mode_t cmask) : 파일 또는 디렉토리가 생성될 때에 불필요하게 많은 권한을 갖지 않도록 통제하는 함수, umask(022) 이런 식으로 씀
- mode_t umask(mode_t cmask) : 파일 또는 디렉토리가 생성될 때에 불필요하게 많은 권한을 갖지 않도록 통제하는 함수, umask(022) 이런 식으로 씀
- 권한 변경 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- int chmod(const char *pathname, mode_t mode) : 특정 파일 권한 변경
- int fchmod(int filedes, mode_t mode) : 열려있는 파일 권한 변경
- process effective user ID == file owner ID 또는 superuser여야 권한 변경이 가능
- &~ 는 이 권한 제외, | 는 이 권한 포함. 원래 있던 권한에 추가하고 싶으면 statbuf.st_mode &~ S_IWGRP
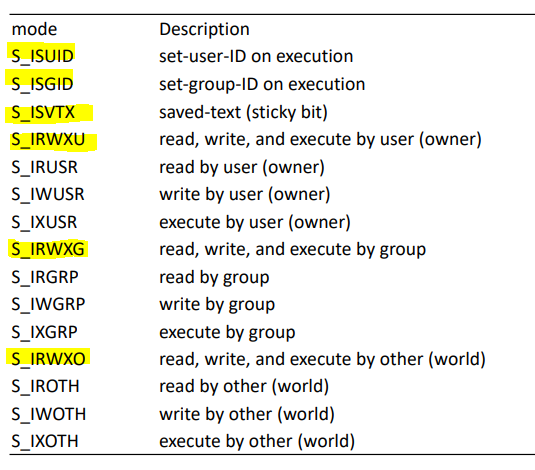
- user ID / group ID 변경 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- int chown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group) : 특정 파일의 user/group ID 변경
- int fchown(int filedes, uid_t owner, gid_t group) : 열린 파일의 user/group ID 변경
- int lchown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group) : symbolic link 자체의 정보 변경
- superuser 만이 file의 owner를 바꿀 수 있다.
파일 링킹 / 복사 / 링크 제거 ..
관련 함수 : link(), unlink(), symlink(), readlink(), remove()
- 파일 링크 생성 / 제거 (hard link / symlink) ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- int link(const char *existingpath, const char *newpath)
- 존재하는 파일에 hard link 생성
- creates a new directory entry, newpath that references the existing file existingpath
- link count 증가
- 같은 file system 내부에서만 링크 형성 가능
- int unlink(const char *pathname)
- Removes the directory entry
- Decrements the link count -> count가 0이 되면 file content is deleted
- 다른 프로세스가 열고 있으면 content는 제거 안됨
- int symlink(const char *actualpath, const char *sympath)
- create a new directory entry, sympath that points to actualpath
- file/directory 실제로 없어도 생성 가능
- 다른 file system이어도 생성 가능
- Dangling link : 없는 파일에 생성 / 원본 파일 없어져도 point
- int remove(const char *pathname)
- file은 unlink, directory는 rmdir
- int link(const char *existingpath, const char *newpath)
- symbolic link 읽기 ( return number of bytes read : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- ssize_t readlink(const char *pathname, char *buf, size_t bufsize)
- symbolic link의 origianl 파일명을 buf에 저장 (buf size가 충분해야 함)
- 읽어들인 buffer 수 return, error 시 -1 return ( symbolic link 아니면 error )
- ssize_t readlink(const char *pathname, char *buf, size_t bufsize)
관련 정보
- cp vs ln vs ln -s
- hard link : inode를 가리킴, 같은 file system 내에 있어야 함, superuser만 directory에 hardlink 만들 수 있음
- symbolic link : 다른 file system이어도 OK, 누구든 directory에 symbolic link 만들 수 있음, dangling link
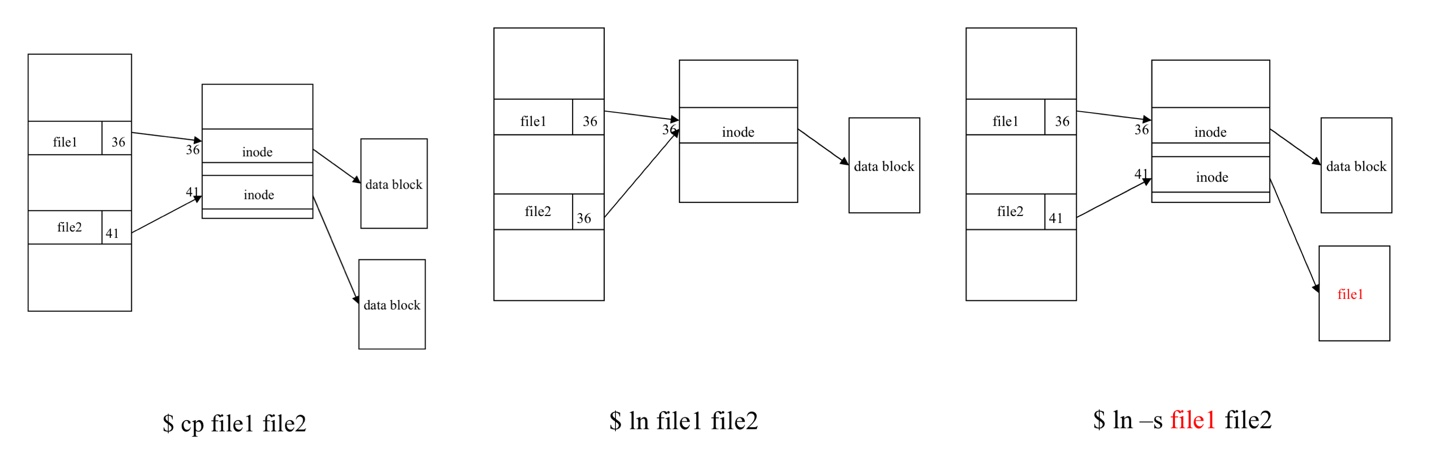
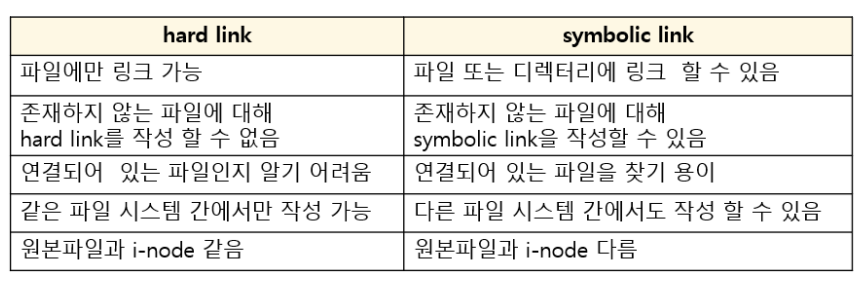
파일 이름 / 위치 변경
관련 함수 : rename()
- 파일 이름/위치 변경 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <stdio.h>
- int rename(const char *oldname, const char *newname)
- command : cp -> move 시 ( mv filename path ) , rename 시 ( mv existfilename newfilename )
- oldname과 newname이 같은 file system에 존재해야 함
- int rename(const char *oldname, const char *newname)
파일 시간 변경
관련 정보 :
- time 종류
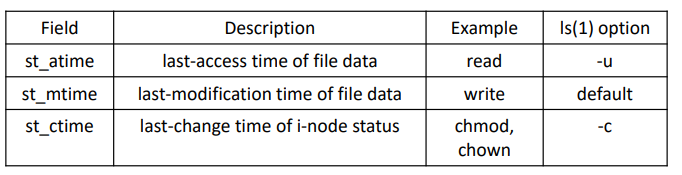
- st_atime : last-access time of file data
- st_mtime : last-modification time of file data
- st_ctime : last-change time of i-node status
- struct utimbuf
struct utimbuf{
time_t actime;
time_t modtime;
}관련 함수 : utime()
- 파일 시간 변경 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <utime.h>
- int utime(const char *pathname, const struct utimbuf *times)
- times == NULL 이면 current time으로 설정
- st_ctime은 utime이 호출되면 자동적으로 update (현재 시각으로)
- int utime(const char *pathname, const struct utimbuf *times)
directory 생성 / 제거
관련 함수 : mkdir(), rmdir()
- directory 생성 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <sys/stat.h>
- int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode)
- create a new empty directory
- dot & dot-dot은 자동 생성
- int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode)
- directory 제거 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- int rmdir(const char *pathname)
- Delete an empty directory
- int rmdir(const char *pathname)
directory read
관련 정보
- Write permission bits for a directory
- Means that we can create/remove files in the directory
- Does not mean that we can write to the directory itself.
- We need some APIs that can deal with directory itself.
- DIR
- represents a directory stream
- <dirent.h>
- struct dirent
struct dirent{
ino_t d_ino; /* i-node number */
char d_name[NAME_MAX+1]; /* null-terminated filename */
}
관련 함수 : opendir(), closedir(), readdir(), rewinddir()
- directory 열/닫기 ( return pointer : OK / NULL : error ) ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <dirent.h>
- DIR *opendir(const char *pathname)
- int closedir(DIR *dp)
- directory entry 읽기 ( return pointer : OK / NULL : end of directory or error)
- #include <dirent.h>
- struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dp)
- directory entry를 읽어와서 dirent struct 반환
- 순서
- 한 번 call하면 첫번째 directory entry를 읽음
- 1번 과정이 끝난 후 directory pointer가 다음 entry로 넘어감
- directory의 끝이라면 NULL return
- void rewinddir(DIR *dp)
- directory pointer를 처음으로 돌림
- struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dp)
working directory
관련 함수 : chdir()&fchdir(), getcwd()
- 현재 working directory 변경 ( return 0 : OK / -1 : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- int chdir(const char *pathname)
- int fchdir(int filedes)
- .c 파일로 실행시키면 shell의 current working directory는 변경 x
- shell은 기본적으로 각각의 program을 서로 독립적인 process로 실행하기 때문
- shell의 current working process를 변경하고 싶다면 built-in command인 "cd" 사용
- 현재 working directory 확인 ( return buf : OK / NULL : error )
- #include <unistd.h>
- char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size)
- size 길이의 buf에 경로 저장 ( size가 경로 + NULL을 수용 가능한 크기여야 함 )
- 절대 경로 반환
- char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size)
4. Time and date
summary
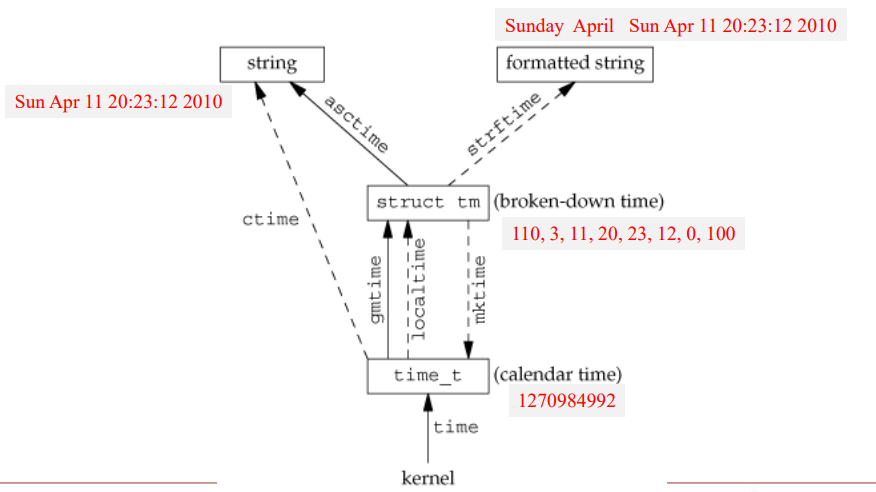
time(), gettimeofday()
- time_t time(time_t *calptr) -> return value of time : OK, -1 : error
- 1970.1.1 00:00 기준으로 seconds return
- int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tp, void *tzp) -> return 0 always
- time()보다 높은 resolution (microsecond)
- 두번째 인자인 tzp는 timezone set인데 현재는 안쓰이므로 NULL로 설정
- struct timeval { time_t tv_sec; long tv_usec; }
gmtime(), localtime()
- tm structure
- tm_sec은 윤초 때문에 59가 아님 (윤초 : 지구 자전 때문에 시간 보정을 위해 사용)
- tm_mon은 0이 1월, tm_wday도 0이 일요일
- tm_year은 현재 - 1900 ex) 2022 = 122 로 출력됨

- struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *calptr) -> return pointer to broken-down time
- UTC 기준 calender time
- struct tm *localtime(const time_t *calptr) -> return pointer to broken-down time
- calender time 을 local time으로 바꿔줌
mktime()
- time_t mktime(struct tm *tmptr) -> return calendar time : OK / -1 : error
- broken-down time -> time_t
asctime(), ctime()
- char *asctime(const struct tm *tmptr) -> return pointer to null-terminated string
- char *ctime(const time_t *calptr) -> return pointer to null-terminated string
- 두 함수 모두26-byte string으로 표현 (data(1) command와 비슷함)
strftime()
- size_t strftime(char *buf, size_t maxsize, const char *format, const struct tm *tmptr) -> return number of characters stored in array if room, 0 otherwise
%A, %B, %c %C
5. Process control
process
- process
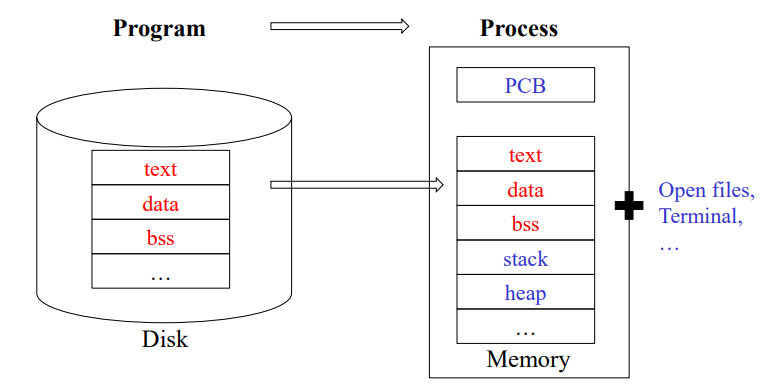
- a program in execution
- program image(text, data, stack, heap) + environment(kernel data structure, address space, open files...)
- text : 작성된 코드 (기계어 포함)
- data : 전역 변수, 정적 변수, 배열, 구조체 .. ( 초기화 O )
- bss : 초기화 x 데이터
- ------------ in disk -----------------
- heap : 동적 할당
- stack : 지역 변수, 매개 변수, 복귀 번지 ..
- PCB
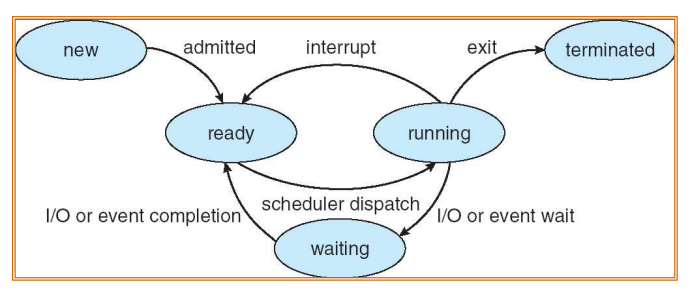
- process state
- process identifiers ( PID )
- every process has a unique process ID -> process 종료 시 재사용 가능
- process 0 (scheduler process or swapper) : part of kernel, system process
- process 1 (init process)
- invoked at the end of the bootstrap procedure
- initialize the UNIX system with /etc/rc* or /etc/inittab -> 읽고 시스템을 다중 사용자 형태로
- 죽지 않음
- speruser 권한을 가지고 실행됨
process 생성 - fork(), vfork()
- pid_t fork(void)
- Create a child process
- 한 번 call하는데 두 번 return
- parent와 child는 fork()를 call한 지점에서 실행 지속
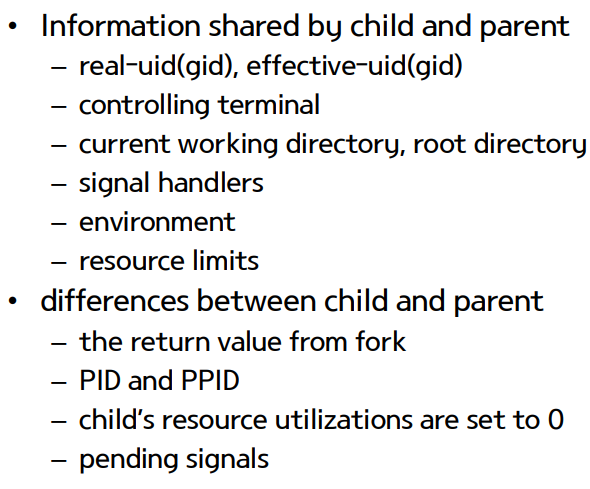
- child copy : parent's data, heap, stack -> 처음엔 공유하다가 변경 시 분리 | share : text, open files
- fork 실패 이유 : system 내부에 이미 너무 많은 process, real user ID에 할당된 process 개수 초과
- fork 사용
- A process wants to duplicate itself : 동시에 다른 section 수행, network server에 자주 쓰임
- A process wants to execute a different program : child는 fork()에서 return 하자마자 exec(), shell에서 자주 씀
- pid_t vfork(void)
- fork()의 2번째 사용 목적에 알맞음
- 부모 process의 address space를 공유함 -> race condition이 발생하지 않도록 부모는 block
- child runs first 를 보장함
process 종료 - exit()
- void exit(int status), void _Exit(int status), void _exit(int status)
- normal program termination & value of status is returned to the parent
- exit vs _Exit, _ exit
- _ 붙은 함수는 즉시 kernel로 return
- exit()는 cleanup processing(open streams are flushed and closed)을 거친 후 kernel로 return
- process termination (둘 다 kernel에서는 같은 동작 수행)
- normal termination
- return from main, calling exit & _Exit & _exit
- termination status : exit status & return value가 termination status로 바뀜
- abnormal termination
- calling abort, receipt of a signal
- termination status : kernel이 비정상 종료의 이유를 나타내는 termination status를 만듦
- termination status 존재 이유는 부모에게 어떻게 종료되었는지를 알리기 위해서
- zombie state
- kernel이 정보를 유지하고 있는 상태. 단, PID & termination status, CPU usage time 만 유지
- parent가 먼저 종료하면 init process가 parent가 돼서 wait()후 termination status를 처리해줌
- normal termination
process 대기 - wait(), waitpid(), MACRO
- wait() & waitpid()를 호출하면 children이 running 중일 때 block, child 없으면 error
- pid_t wait(int *statloc) -> return child process ID : OK / -1 : error
- 이미 종료해서 좀비 상태인 child가 있으면 child의 상태와 함께 return
- 아직 종료 안됐으면 block
- 여러 child가 있으면 아무거나 하나 기다림
- staloc에다 child의 termination status를 저장함
- pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *statloc, int options) -> return child process ID : OK / 0 or -1 : error
- pid argument
- pid == -1 : 아무나
- pid > 0 : pid 일치하는 process
- pid == 0 : 같은 group process
- pid < 0 : wait child whose process group ID equals the absolute value of pid
- option argument
- WNOHANG : 원하는 pid가 종료하지 않았다면 not block
- WUNTRACES : 원하는 pid가 정지되어 있으면 not block
- pid argument
- MACRO

program 실행 - exec() ( return -1 : error / no return : success )
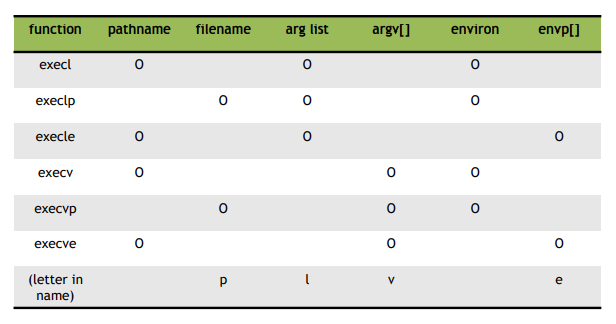
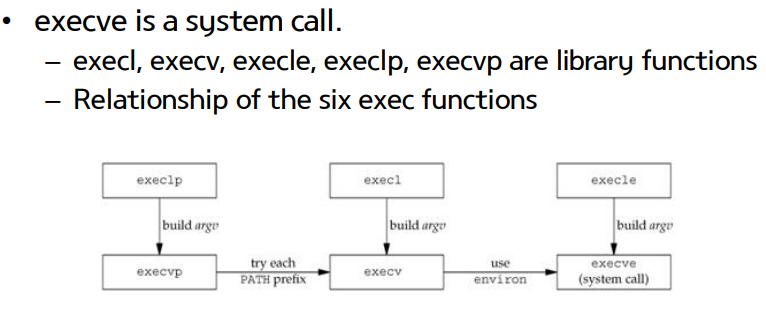
- program 실행
- process가 call하면 process는 new program으로 완전히 대체
- (text, data) 만 바꿈
- pid는 변하지 않음
- new program main() 실행
- 인자 : pathname/filename, list/vector, environ/envp[]
- pathname(-) / filename(p)
- filename은 PATH가 미리 설정되어 있어야함
- arg list(l) / arg vector(v)
- 둘 다 맨 뒤에 NULL pointer 필수
- environ(-) / envp[](e)
- envp[] 맨 뒤에 NULL pointer((char*) 0 or NULL) 필수
- pathname(-) / filename(p)
- execve만 system call
- process가 call하면 process는 new program으로 완전히 대체
Proxy server 1
- Network programming : involves writing programs that communicate with other programs across a computer network
- Unix/Linux 제공 low-level network services : TCP/IP,UDP
- API : Socket, XTI
- client&server exaples : Web client(browser) & server, FTP client & server, telnet client & server
- Proxy server
- 인터넷의 캐시 프로그램으로 최근에 가져온 자료들을 보관하는 저장장소를 의미
- 같은 자료를 다시 요구할 경우 Proxy 내의 캐시에 있는 자료를 제공함으로써 자료가 빠르게 전송
- 사용자는 Proxy를 사용해서 자료를 받아 오겠다는 사실을 호스트에 알려주어야 proxy 사용 가능
- 더 느려질 수도 있음
1. Cache implement
- Cache의 기능 : Original server의 데이터를 저장함으로써 network delay 감소, HIT/MISS 판별
- Hash function
- 임의의 길이의 데이터를 고정된 길이의 데이터로 매핑하는 함수
- 종류 : MD5, SHA, CRC32
- Multiple processing
- on-demand manner (client가 요청하는 경우만 server 생성)
- main server는 child와 client를 이어주는 역할
- child가 종료되면 parent는 신호를 받음 -> signal handling
2. Proxy server implementation
- 단계
- Simple server/client implementation -> socket 통신
- HTTP request/response handling
- protocol : 통신을 원하는 개체간에 어떻게 통신할 것인가를 약속한 규약
- protocol stack : 특정 machine에서 사용하는 protocol list
- HTTP request format -> ppt
- HTTP response format -> ppt
- Proxy
- Signal handling
- Proxy server implementation