chapter 1
주요 주제
인터넷이란?
네트워크 엣지
네트워크 코어
delay, loss, throughput in networks
protocol layers, service models
보안
역사
1.1 What is the Internet?
인터넷이란?
구성 요소 3가지 : computing devices, communication links, packet switches
computing devices :
- host = end system
- running network apps
communication links
- (유선) fiber, copper,/ (무선) radio, satellite
- satellite와 radio의 차이 : satelite는 단말과 바로 통신하면 단말의 파워가 아주 세야함, 가로막는 게 없으므로 고주파 (직진성 강한 주파수) 사용 가능
- transmission rate : bandwidth
packet switches : routers and switches
프로토콜이란?
프로토콜은 컴퓨터 내부에서, 또는 컴퓨터 사이에서 데이터의 교환 방식을 정의하는 규칙 체계입니다.
1.2 network edge : end systems, access networks, links
network 구성 요소 : network edge, access networks & physical media, network core
Access network
end system이 edge router에 연결하기 위해선? 개인/기관/기지국 망 이용 -> bandwidth 및 share 여부 고려해야함
1. digital subscrber line (DSL) : 기존의 전화망 사용
- 컴퓨터 -- DSL modem -- 기존의 전화망 (집)///(야외) ------------- DSLAM ---- 기존 전화 / 인터넷 트래픽 분배
- DSLAM 부분에서 다른 집들의 전화선과 합쳐짐
- 특징 : downstream transmission rate가 더 높음
2. cable network
- 컴퓨터 -- cable modem (집)//-------(다른 집들과 공유)---------- CMTS(cable modem termination system) ---- ISP
- frequency division multimplexing : 대역폭이 넓어서 선 하나를 나눠씀
3. Home network
- 집 내부에 switch가 있어서 다른 end system들과 연결됨.
- switch --- cable or DSL modem // --- to/from headend or central office
Ethernet (Enterprise access networks)
- 회사나 대학 등에서 자주 쓰임
Wireless access networks
- shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station aka "access point"
- 종류
- wireless LANs : 집 wifi 개념
- wide-area wireless access : 공공 wifi 개념
Host : sends packets of data
- packet transmission delay = 패킷의 길이 / 링크의 속도(도로의 폭) = L/R (sec)
- 패킷이 나오는데 걸리는 시간
Physical media
용어 : bit(운반 데이터), physical link(운반해주는 선), guided media(정해진 경로->유선),
unguided media(퍼져나가는 형태->무선), twisted pair(TP) (유선)
- coax, fiber
- coax cable : 광섬유 사용 전 많이 씀, R이 큼
- fiber optic cable
- R값이 매우 크고 error가 거의 없음
- 가격 저렴하지만 광신호 -> 전기 신호로 바꾸는 비용이 비쌈
- 전반사가 일어나는 범위 내에서 여러 파장을 이용함
- radio
- 무선
- type : terrestrial microwave ( LAN -> 공유기 필요, wide-area -> 기지국 필요), satellite(-> propagation delay)
- 다양한 대역폭 존재
- 주파수가 너무 높으면(적외선~자외선) : 몸에 해로움 & 직진성이 높아서 장애물이 있으면 무용지물
- 주파수가 너무 낮으면 : 파장이 길어서 안테나도 길어져야 함 => 불편
- 안테나의 길이 : d=λ2
1.3 network core : packet switching, circuit switching, network structure
Packet-switching
데이터를 패킷 단위로 쪼개서 전송하는 방식
: store-and-forward
- 다음 링크로 전송하기 전에 저장을 한 뒤 전달하는 방식
- end-end delay : NxLR
: queueing delay, loss
- queueing delay : store-forward에서 store 했다가 뽑아내는 시간
- loss : 대기 패킷 버퍼가 꽉 차서 store 불가 => buffer overflow 나서 정보 유실
Two key network-core functions : routing & forwarding
- routing (머리쓰기) : 목적지까지 어떤 루트를 사용할지 -> 경로를 찾고 만드는 부분
- forwarding (몸쓰기) : 찾은 경로를 따라 가는 것
- routing algorithm : routing에서 table을 생성하고 forwarding에서 table을 읽고 움직임
- 다음 지점은 다음 지점에 가봐야지 확인 가능 ( 해당 지점마다 header value에 따른 output link 있음 )
Alternative core : circuit switching ( -> packet switching의 대안 방법 )
- 하나의 회선을 할당받아 데이터를 주고받는 방식
- 독점적이기 때문에 성능이 좋지만 비용이 비싸고 여러 명이 쓰기 힘듦
- 방식 : FDM, TDM
- FDM (frequency division multitasking) : 할당된 대역폭을 나누어 사용하는 방식
- TDM (time division multitasking) : 할당된 대역폭을 시간단위로 나누어 사용하는 방식
Packet switching VS Circuit switching
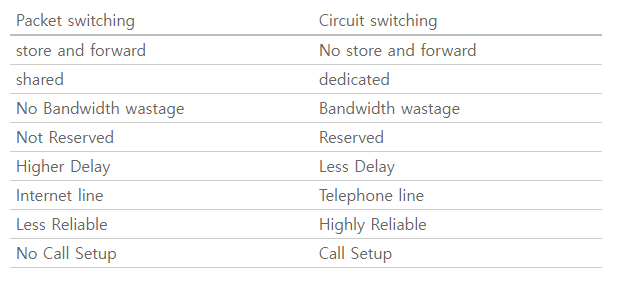
- packet switching은 bursty data에 좋음
Internet structure : network of networks
End system들은 access ISPs 를 통해서 인터넷에 연결됨.
-> access ISP 들은 상호연결되어야 소통 가능 => n(n+1)2 는 너무 많음 ( O(n2) connections )
-> solution : 중간에 switch를 놓으면 됨 ( O(n) connections ) ( global ISP )
solution ISP의 변화 >
- ISP 여러 구역으로 쪼개짐
- ISP 그룹 간 연결(IXP) 생성
- network가 점점 부분부분 생김
1.4 delay, loss, throughput in networks
delay : transmission delay ( LR ), packets queuing delay
loss : packet arrival rate > packet capacity
Four sources of packet delay => 홉(node) 개수만큼 반복
>> dnodal=dproc+dqueue+dtrans+dprop
- dproc : nodal processing, node에 들어온 뒤 처리 시간
- dqueue : queueing delay, queue에서 대기하는 시간
- dtrans : transmission delay, LR
- dprop : propagation delay, ds ( d=length of physical link, s=propagation speed )
Caravan analogy
- propagation delay << transmission delay (propagation 거리가 가깝거나 link 속도(R)이 저속일 때)
- 맨 뒤의 bit는 transmission 중인데 첫번째 bit는 이미 도착해있는 현상 발생
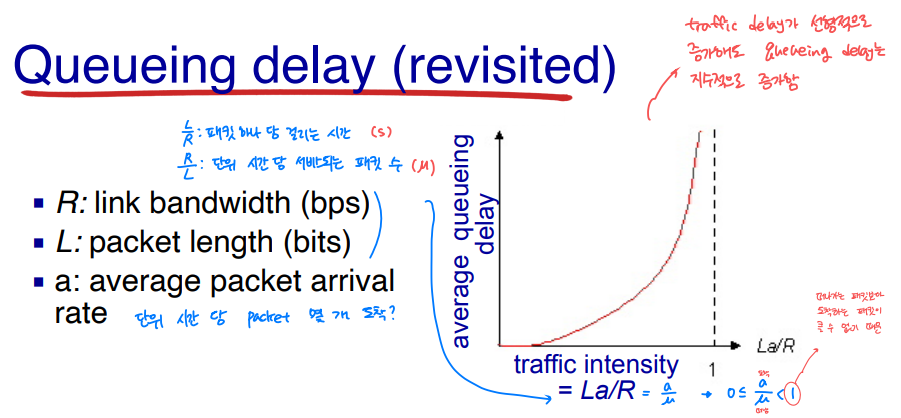
"Real" Internet delays and routes
- traceroute program : 패킷이 목적지까지 갈 때 거치는 라우터와 시간을 알아볼 수 있음
- TTL 값을 1로 설정하고 전송 -> 0 되면 돌아옴 -> 하나씩 늘리면서 반복함
- 라우터의 받는 IP와 보내는 IP가 다를 수 있으므로 실질적으론 보내는 IP를 파악하는 것
- 맨 마지막에는 라우터가 아니므로 UDP 포트를 아주 크게 설정해서 고의 에러로 파악
Packet loss
- queue에서 발생 -> 도착하는 패킷 > 나가는 패킷 일 때 buffer overflow가 발생해서 패킷이 유실됨
Throughput
- 처리율
- 단위는 bits/time unit
- instantaneous(순간)와 average(평균)
- end-end througput은 작은 R에 따라 결정됨 (병목현상)
1.5 protocol layers, service models
layers
- 네트워크는 다음과 같은 복잡한 요소들로 이루어져 있음
- hosts, routers, links of various media, applications, protocols, hardware&software
- 복잡한 시스템을 다루기 위해서 분할을 함 ( but layer가 너무 많으면 오버헤드 )
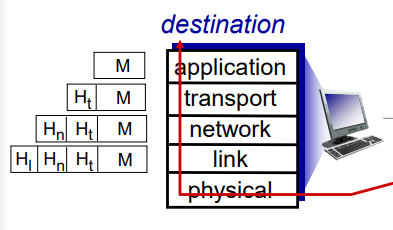
- Internet protocol stack : application(FTP, SMTP, HTTP), transport(TCP, UDP), network(IP, routing protocols), link(Ethernet, WiFi, PPP), physical(bits "on the wire")
- ISO/OSI 표준에는 presentation(encoding, 암호화), session(시간적인 개념)도 있지만 실제로는 안씀
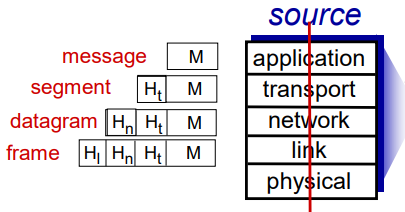
Encapsulation
- layer를 지날 때마다 header가 붙으면서 packaging 됨 => 오버헤드
- 실제로는 message가 길어지면 segmentation 해서 자름
- 목적지에 도착하면 decapsulation
1.6 networks under attack : security
network security
- attack & defend
- attack
- malware : virus, worm, spyware malware, 랜섬웨어, DDoS botnet
- DoS : hosts에게 바이러스를 심어두고 target에게 동시에 packet을 전송함->target(server) 고장
- solution : 앞 단에 url 적은 가벼운 페이지로 방패막이
- packet "sniffing" : 패킷 염탐
- IP spoofing : 특정 필드의 값을 바꿈 -> 악용시에는 주로 보내는 사람 주소를 바꿔서 자기가 안 보낸 척 함