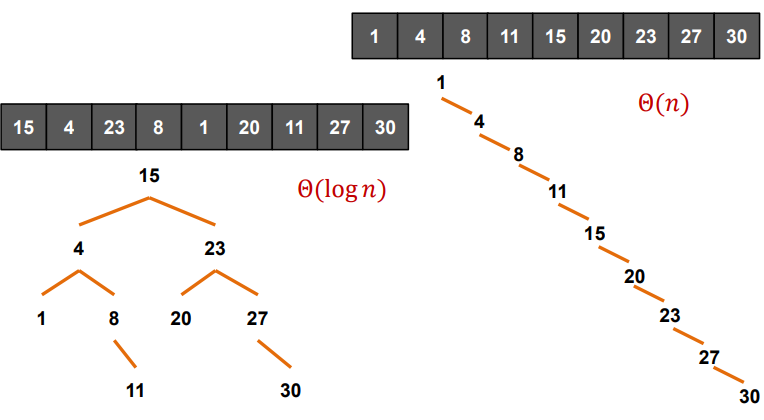
이진 탐색 ( Binary Search )
이진 탐색이란?
정렬되어있는 배열에서 사용
처음과 끝 인덱스의 중간 지점보다 찾고자하는 값이
- 작으면 : 처음 = 중간, 끝은 그대로
- 크면 : 처음은 그대로, 끝 = 중간
- 같으면 : 반환
이진 탐색 vs 이진 탐색(검색) 트리
- 임의의 데이터들 -> 순서대로 정렬한 후 이진 탐색
- 데이터를 입력할 때부터 정렬 -> 이진 탐색(검색) 트리
코드
python 코드
####### Binary Search ######
import random
from timeit import default_timer as timer
def binary_search(x, v):
start = 0
end = len(x) - 1
while start<=end:
mid = (start+end) // 2
if x[mid] == v : return mid
elif x[mid] < v : start = mid + 1
else: end = mid - 1
return -1
x = random.sample(range(5000), 1000)
x.sort()
value = x[800]
start = timer()
index = binary_search (x, value)
print(timer() - start)
print('value ', value, 'found ', index)
print(True if index >=0 and x[index] == value else False)
c++ 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int A[10];
int binary_search(int target)
{
int start = 0, end = 9;
int mid;
while (start <= end)
{
mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (A[mid] == target) return mid;
else if (A[mid] > target) end = mid - 1;
else start = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
A[i] = rand() % 100;
}
sort(A, A + 10);
int index = binary_search(A[3]);
cout << "A[3] = " << A[3] << endl;
if (index > -1)
cout << "index = " << index << ' ' << "A[index] = " << A[index] << endl;
else
cout << "error";
}
이진 검색 트리 ( Binary Search Tree )
이진 검색 트리란?
왼쪽 자식은 부모보다 작고 오른쪽 자식은 부모보다 큼
- 각 노드는 하나의 키 값을 가진다.
- 각 노드의 키 값은 모두 달라야 한다.
- 각 노드는 최대 두 개의 자식 노드를 갖는다.
- 각 노드의 키 값은 왼쪽의 모든 노드의 키 값보다 크고 오른쪽의 모든 노드의 키 값보다 작다.
Insert, Search, Delete
Insert
작으면 왼쪽 크면 오른쪽으로 넣음
Search
작으면 왼쪽 크면 오른쪽 찾음
Delete
1. 자식 노드가 0개인 경우 : 그냥 지움
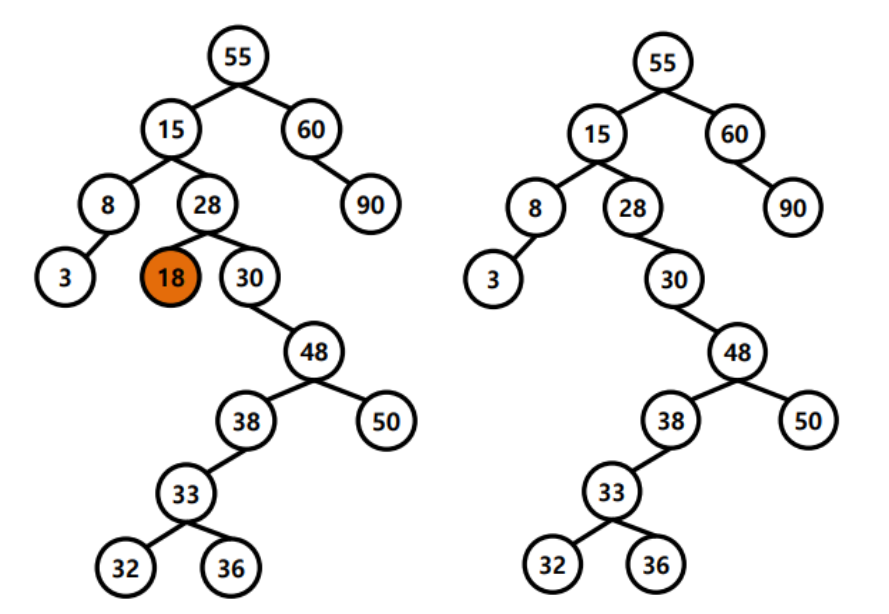
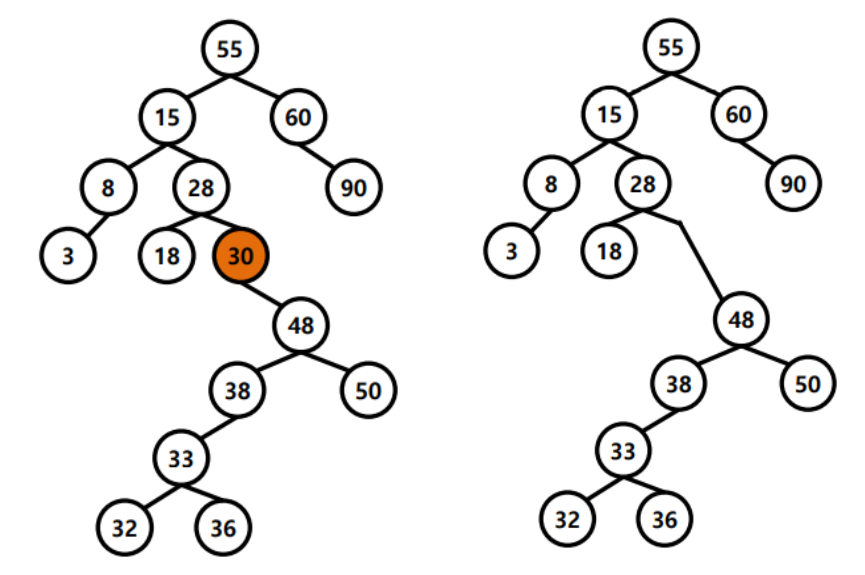
2. 자식 노드가 1개인 경우 : 부모와 자식 이어줌
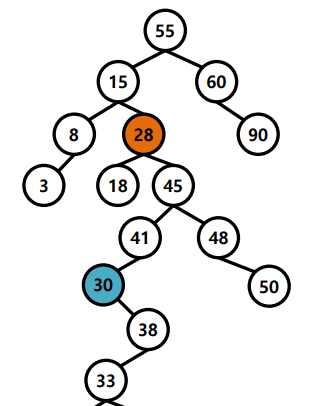
3. 자식 노드가 2개인 경우 :
- 오른쪽 자식에서 제일 작은 노드를 찾는다. ( 왼쪽 자식보다 큰 노드 중에서 가장 작은 노드 )
- delete하고 위에서 찾은 노드를 위로 올린다.
- 빈 노드는 자식이 최대 하나이므로 위에서 설명한 것처럼 잇는다.
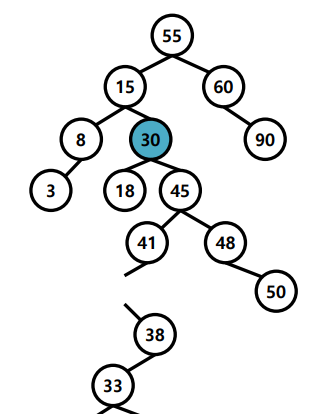

이진 검색 트리의 단점
데이터 입력 순서에 따라 성능이 달라진다.
python 코드
import random
from timeit import default_timer as timer
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, key, parent):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.parent = parent
def insert(node, key, parent):
if node is None :
node = Node(key, parent)
elif key < node.key :
node.left = insert(node.left, key, node)
else : node.right = insert(node.right, key, node)
return node
def search(node, key):
if node is None or node.key == key: return node
if key < node.key : return search(node.left, key)
return search(node.right, key)
def delete_node(node):
if node.left is None and node.right is None :
return None
elif node.left is not None and node.right is None :
return node.left
elif node.left is None and node.right is not Node :
return node.right
else:
s = node.right
while s.left is not None :
sparent = s
s = s.left
node.key = s.key
if s == node.right :
s.right.parent = node
node.right = s.right
else :
s.right.parent = sparent
sparent.left = s.right
return node
def delete(node) :
if node.parent is None : node = None
elif node is node.parent.left : node.parent.left = delete_node(node)
else : node.parent.right = delete_node(node)
x = [10,20,30]
value = 30
root = None
for i in x:
root = insert(root, i, None)
start = timer()
found = search(root, value)
print(timer()-start)
if found is not None:
print('value', value, 'found', found.key)
print(True if found.key == value else False)
delete(search(root, value))
found = search(root, value)
AVL-트리
AVL-트리란?
- 가장 초기에 나온 균형 잡힌 이진 검색 트리
- 균형 이진 트리 : 각 노드의 왼쪽/오른쪽 서브 트리의 높이 차가 1 이하
- 높이 차가 2 이상이 될 경우 단일 회전 / 이중 회전
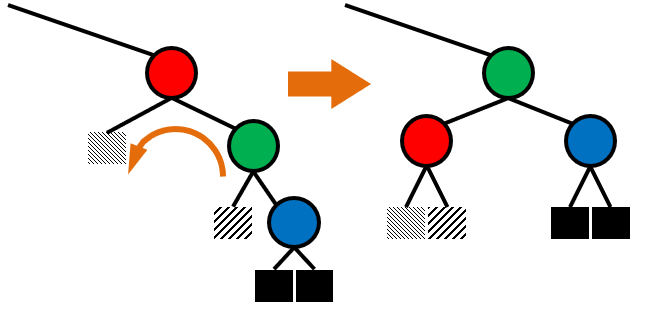
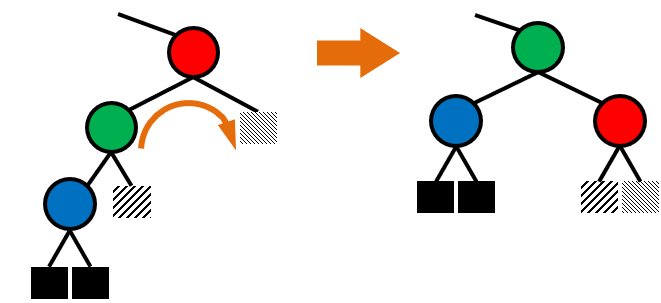
회전
- 단일 회전
- 자식 노드가 존재하는 부모 노드의 방향이 동일한 경우
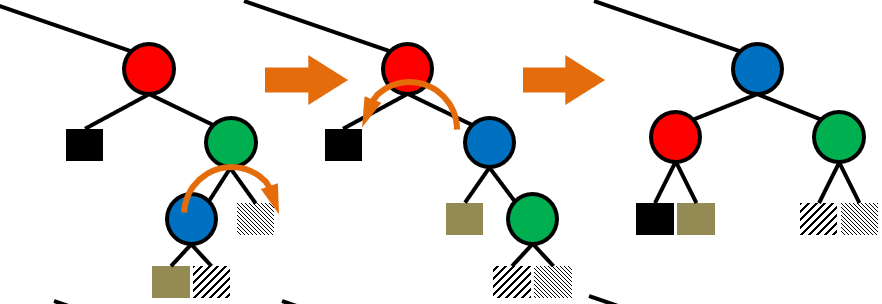
- 이중 회전
- 자식 노드가 존재하는 부모 노드의 방향이 동일하지 않은 경우
- 회전을 통해 방향을 일치 시킨 후 단일 회전
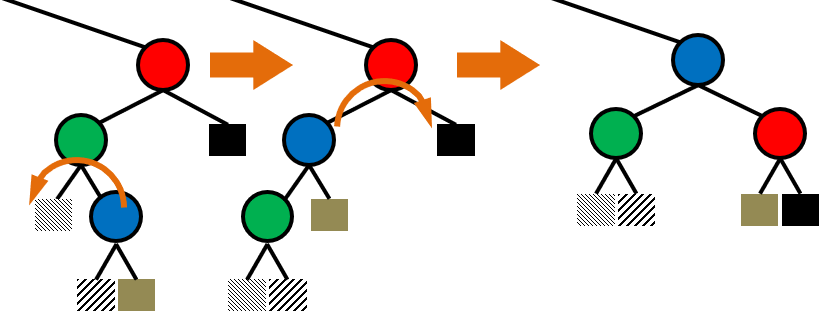
스플레이 트리
스플레이 트리란?
- 탐색, 삽입, 삭제 시 스플레이를 하는 Tree
- Splay는 Splay tree의 기본이 되는 연산으로, 쿼리에 의해 접근한 노드를 트리 구조에 따라 특정 방식으로 rotate해서 루트까지 끌어올리는 연산 (https://blog.chodaeho.com/posts/2021/splay-tree-1/)
- zig 회전 / zig-zig 회전 / zig-zag 회전
zig 회전
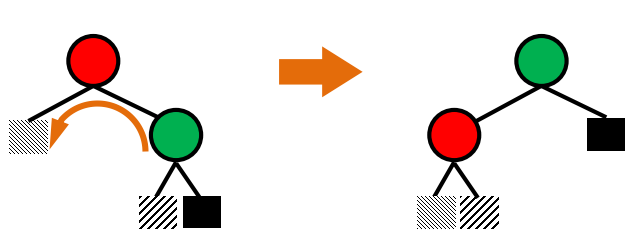
zig-zig 회전
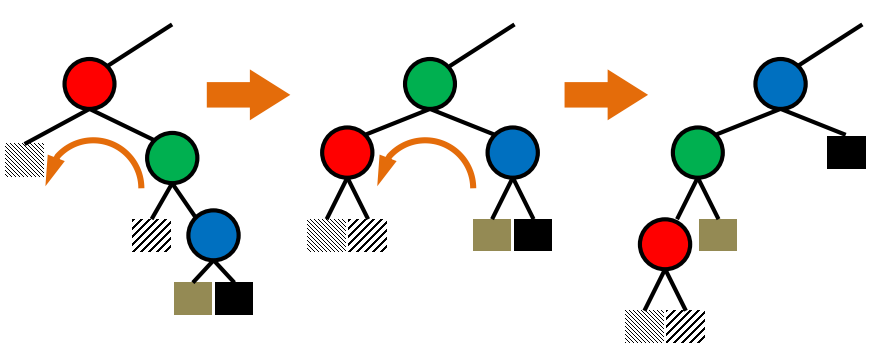
zig-zag 회전
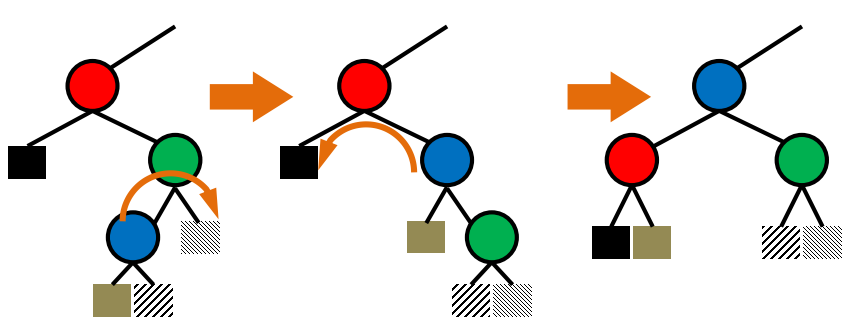
레드 블랙 트리 (Red Black Tree)
레드 블랙 트리란?
- root는 블랙
- 완전 이진 트리 ( NIL 사용 )
- 모든 leaf는 블랙
- 레드의 자식은 블랙 ( 레드 연속 2개 불가 )
- 최소 높이는 모두 블랙인 경우
- 최대 높이는 레드-블랙 교대인 경우
- root - leaf까지의 모든 경로는 같은 개수의 블랙
- 최악의 경우에도 최소 높이의 2배 이하
- 왼쪽 회전 / 오른쪽 회전
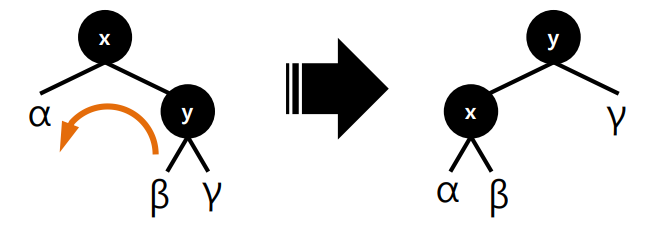
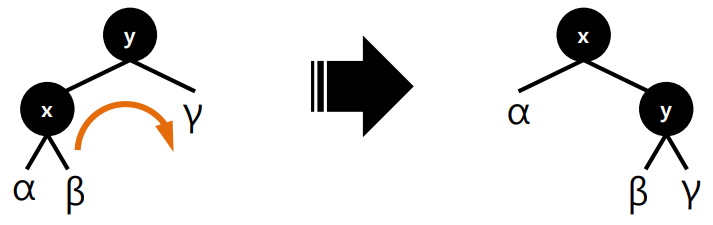
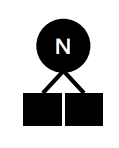
노드 삽입 (N이 새 노드 & 레드 노드)
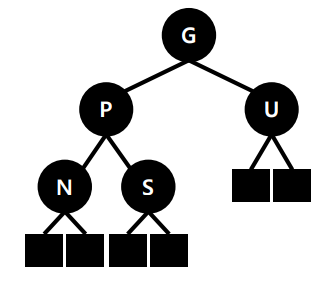
case 1: 빈 트리
- N을 root & 블랙으로
case 2: P가 블랙
- 그냥 삽입
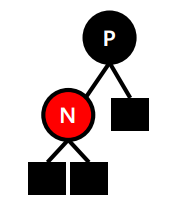
case 3: P가 레드
- case 3-1 : U가 레드
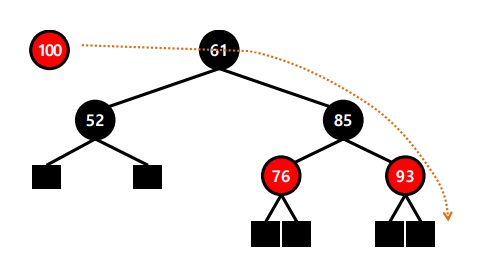
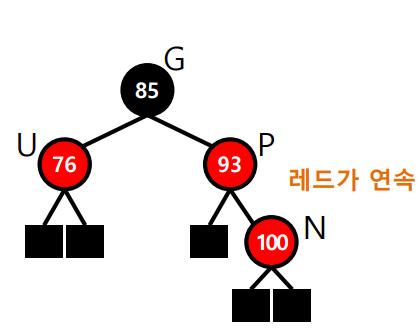
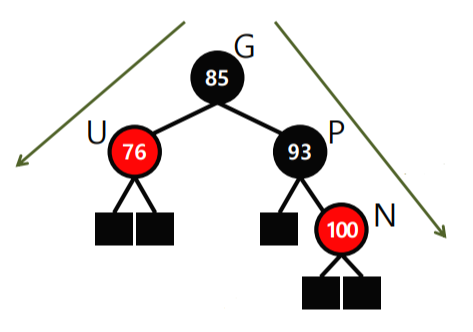
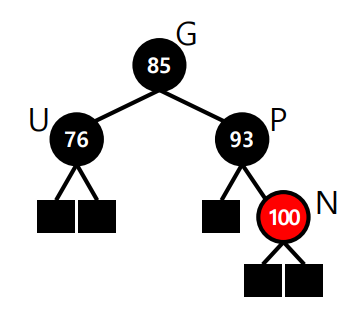
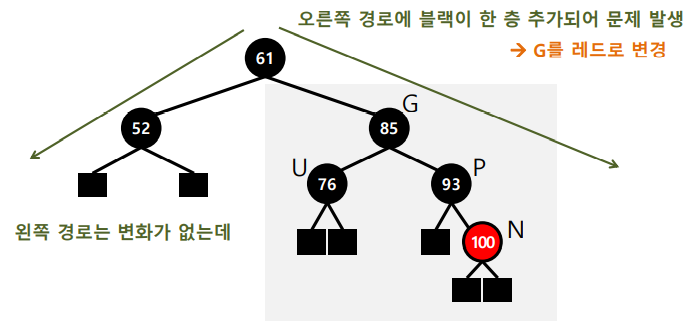

(만약 G가 root라면 3단계까지만 진행해도 됨)
- case 3-2 : U가 블랙
- case 3-2-1 : P가 오른쪽 자식, N이 오른쪽 자식
- case 3-2-2 : P가 오른쪽 자식, N이 왼쪽 자식
- case 3-2-3 : P가 왼쪽 자식, N이 왼쪽 자식
- case 3-2-4 : P가 오른쪽 자식, N이 오른쪽 자식
'22-1학기 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4. 선택 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.04.06 |
|---|---|
| 3. 정렬 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| 2. 점화식과 알고리즘 복잡도 분석 (0) | 2022.03.14 |
| 1. 알고리즘 표기법 (0) | 2022.03.14 |